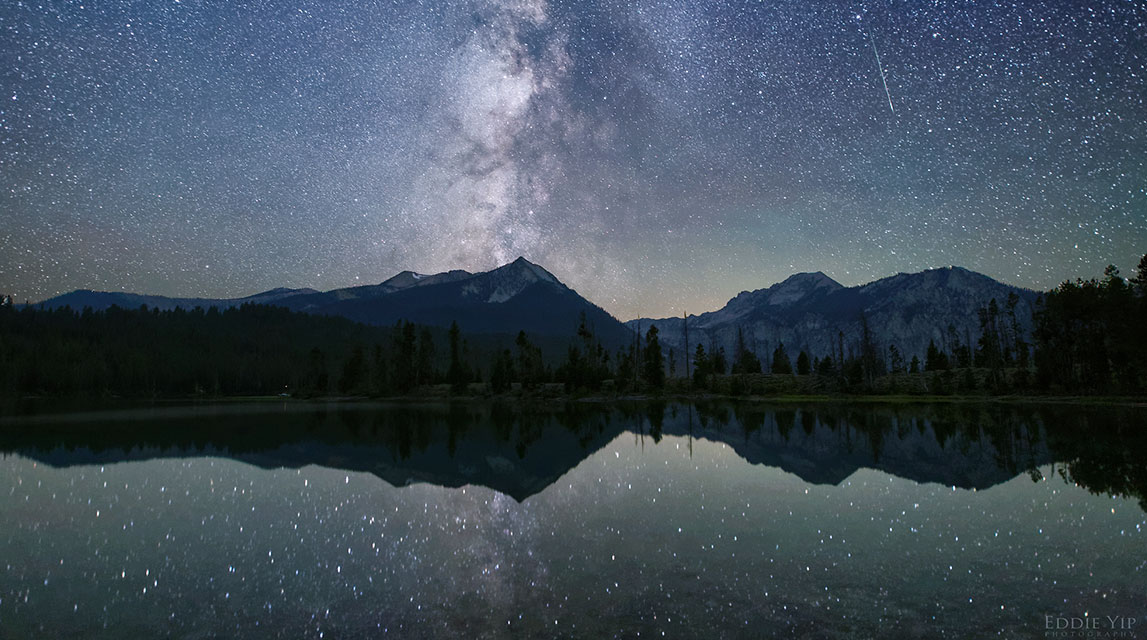

ƒ/2.0, 25s, 20mm, ISO 12800) © Eddie Yip
During this period the moon will reach its first quarter phase on Friday February 23rd. At that time the moon will lie 90 degrees east of the sun and will set near 0100 local standard time (LST). This weekend the waxing crescent moon will lie low in the western sky at dusk and will not interfere with meteor observing. The estimated total hourly meteor rates for evening observers this week is 3 as seen from mid-northern latitude (45N) and 5 from the southern tropics (25S). For morning observers the estimated total hourly rates should be near 6 as seen from mid-northern latitudes (45N) and 13 from the southern tropics (25S). The actual rates will also depend on factors such as personal light and motion perception, local weather conditions, alertness and experience in watching meteor activity. Note that the hourly rates listed below are estimates as viewed from dark sky sites away from urban light sources. Observers viewing from urban areas will see less activity as only the brighter meteors will be visible from such locations.
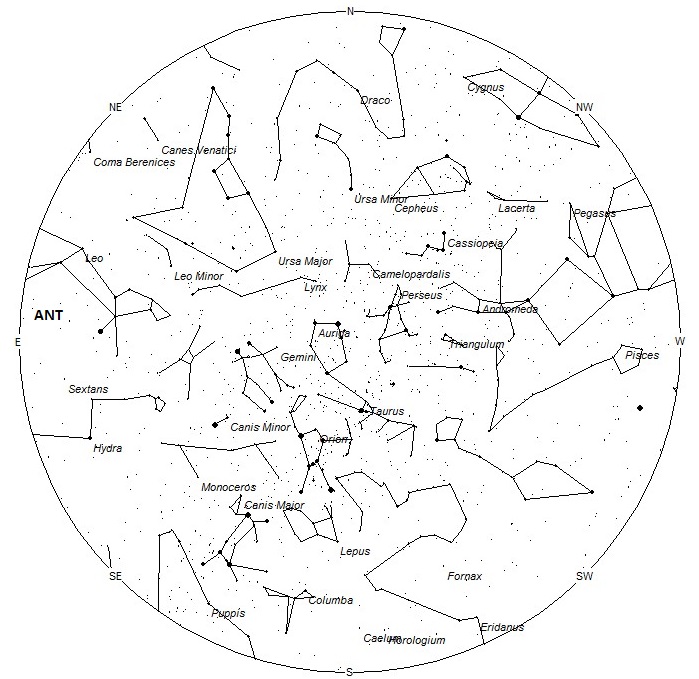
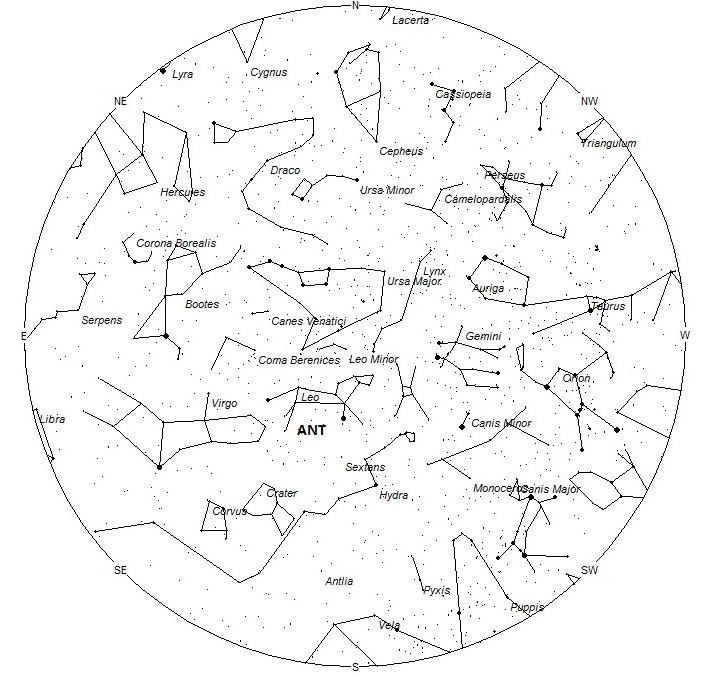
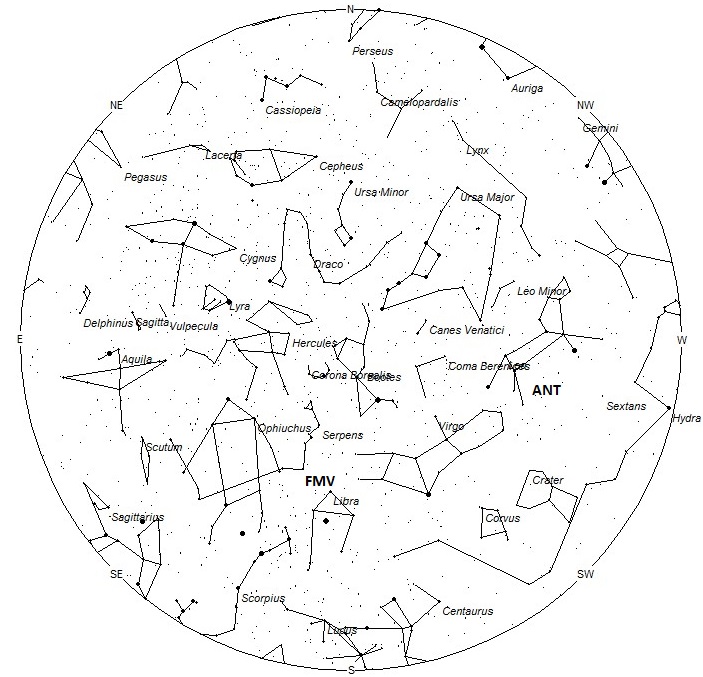
The radiant (the area of the sky where meteors appear to shoot from) positions and rates listed below are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning February 17/18. These positions do not change greatly day to day so the listed coordinates may be used during this entire period. Most star atlases (available at science stores and planetariums) will provide maps with grid lines of the celestial coordinates so that you may find out exactly where these positions are located in the sky. A planisphere or computer planetarium program is also useful in showing the sky at any time of night on any date of the year. Activity from each radiant is best seen when it is positioned highest in the sky, either due north or south along the meridian, depending on your latitude. It must be remembered that meteor activity is rarely seen at the radiant position. Rather they shoot outwards from the radiant so it is best to center your field of view so that the radiant lies near the edge and not the center. Viewing there will allow you to easily trace the path of each meteor back to the radiant (if it is a shower member) or in another direction if it is a sporadic. Meteor activity is not seen from radiants that are located far below the horizon. The positions below are listed in a west to east manner in order of right ascension (celestial longitude). The positions listed first are located further west therefore are accessible earlier in the night while those listed further down the list rise later in the night.
These sources of meteoric activity are expected to be active this week.
.
The center of the large Anthelion (ANT) radiant is currently located at 10:48 (162) +07. This position lies in southern Leo, 10 degrees southeast of the 1st magnitude star known as Regulus (alpha Leonis). Due to the large size of this radiant, Anthelion activity may also appear from western Virgo, and Sextans as well as Leo. This radiant is best placed near 0100 local standard time (LST), when it lies on the meridian and is located highest in the sky. Rates at this time should be near 2 per hour no matter your location. With an entry velocity of 30 km/sec., the average Anthelion meteor would be of slow velocity.
The last of the alpha Centaurids (ACE) are expected this weekend. The radiant is currently located at 14:56 (224) -62. This position lies in southeastern Centaurus, 3 degrees southeast of the zero magnitude star known as Rigel Kentaurus (alpha Centauri). Due to the southern declination of this radiant, these meteors are not well seen in the northern hemisphere. Current rates are expected to be less than 1 no matter your location. These meteors are best seen near 0500 LST when the radiant lies highest above the horizon. At 56 km/sec. the Alpha Centaurids would produce mostly swift meteors.
The February Mu Virginids (FMV) were discovered by Damir Šegon and the Croatian Meteor Network team based on studying SonotaCo and CMN observations (SonotaCo 2007-2011, CMN 2007-2010). These meteors are active from February 16 through March 4 with maximum activity occurring on February 25. The current radiant position lies near 15:28 (232) -05, which actually places it northern Libra, 5 degrees northeast of the 3rd magnitude star known as Zubeneschamali (beta Librae). Rates are expected to be less than 1 per hour no matter your location. These meteors are best seen near 0500 LST when the radiant lies highest above the horizon. At 62 km/sec. the February Mu Virginids would produce mostly swift meteors.
As seen from the mid-northern hemisphere (45N) one would expect to see approximately 6 sporadic meteors per hour during the last hour before dawn as seen from rural observing sites. Evening rates would be near 2 per hour. As seen from the tropical southern latitudes (25S), morning rates would be near 11 per hour as seen from rural observing sites and 4 per hour during the evening hours. Locations between these two extremes would see activity between the listed figures.
| SHOWER | DATE OF MAXIMUM ACTIVITY | CELESTIAL POSITION | ENTRY VELOCITY | CULMINATION | HOURLY RATE | CLASS |
| RA (RA in Deg.) DEC | Km/Sec | Local Standard Time | North-South | |||
| Anthelion (ANT) | – | 10:48 (162) +07 | 30 | 01:00 | 2 – 2 | II |
| alpha Centaurids (ACE) | Feb 08 | 14:56 (224) -62 | 56 | 06:00 | <1 – <1 | II |
| February mu Virginids (FMV) | Feb 25 | 15:28 (232) -05 | 62 | 07:00 | <1 – <1 | IV |
 American Meteor Society
American Meteor Society
Saw a streak of light overhead tonight in South Georgia around 10:15 pm EST…I’m not qualified to call it anything other than possibly a shooting Star.
Slow moving bright light south-west of San Diego. I photographed it but looks like a round blue ball. 9:10pm PST
I saw a large ball of very bright light falling in the sky last night (2-20-18) around 9pm. It was falling in a northerly direction from my location in Palmdale, CA. I was a bright spherical ball – no tail or anything. It fell fast and then disappeared over the hills. Did anyone else see it? I’m curious as to what it was. I’m assuming a meteorite.
Karen and All,
I checked our fireball report table and did not find any other reports that matched yours. We had a couple from the same night but they were seen either too far away or later that night to be associated with the one you saw. February is the most active month for evening fireballs so it is not that surprising you were able to see one. To increase your chances of seeing another one I would suggest viewing during one of the major annual meteor showers. The next one is due to occur on the night of August 12/13 when the Perseid meteor shower reaches maximum activity.
I hope this helps!
Robert Lunsford
I live in Madison, Alabama and on Monday February 19,2018 at 8:48 pm I saw a meteor falling thru the cloudy sky. The meteor had a white greenish tail. I have not been able to find out any information. Do you have any information about this occurrence?
Amelia and All,
Your fireball was widely seen over several southern states. February most active month for evening fireballs so it is not surprising that you witnessed one. You can see a map of other witnesses and their comments at: https://www.amsmeteors.org/members/imo_view/event/2018/677
Robert Lunsford